The Email
===
[Maria Dimou](https://cern.ch/maria)
CERN IT
Prepared for the **"Distributed Computing - a historical perspective"**
Academic Training series
[Event Details](https://indico.cern.ch/event/1052076/)
2022-05-12
[D.Knuth - Let's drop the hyphen](https://www-cs-faculty.stanford.edu/~knuth/email.html)
---
## Contents
Late 1980s - early 1990s
1. Situation with the network.
2. Creativity and liberty in the Internet world.
3. Regulation and hierarchy in European networking.
4. The CERN Email gateway before the Microsoft contract of the late 1990s.
---
### Why talk about the past
1. We have to know **WHY** we did what we did and **HOW** we did it.
2. This helps selecting future choices that work.
3. Required Prerequisites:
* Agreement on _what_ works, i.e. via _proof_ & common _values_.
* Willingness to accept a certain _work culture_ and _ethic_. Example: backwards compatibility and decision-making by consensus.
---
### The era when a dictionary on Computing had just 500 pages

Chandor, Graham, Williamson book printed in 1970, 1981, 1986, still read today(!?)
---
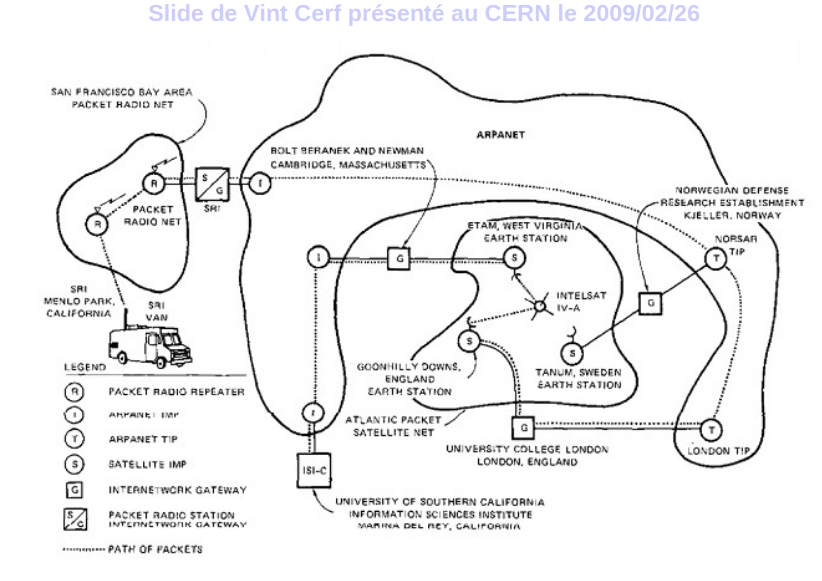
### Internet beginnings - the map
---
### Internet beginnings - the van

---
### Check the table on the next slide
Countries with x in the Spring 1993 Internet Society NEWS magazine Vol.2 No.1
* They have NO international connectivity!
* Most have only Email connectivity.
---

---
### CERN in the 1980s

Extract from Tim Berners-Lee's talk at CERN Conference
"The role of Science in the Information Society" Dec. 2003
[See here his slides in HTML](https://www.w3.org/2003/Talks/1209-rsis-tbl/)
---
### European network standards & organisations
* EUREKA COSINE project
* OSI standard
* RARE organisation
---
### COSINE
* Stands for **C**ooperation for **O**pen **S**ystems **I**nterconnection **N**etworking in **E**urope.
* Eureka Project No. 8, is to create a computer networking infrastructure based on the use of OSI protocols which will provide services to the whole research and development community (academic and commercial) throughout Europe.
* Funded by 19 European countries and the Commission of the European Communities.
* Started in 1986.
* Composed by several Working Groups (WGs).
* In WG3 Maria Dimou represented CERN for Email and Directory Services and Tim Berners-Lee for Information Services.
[H.E.Davies paper 1990](https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-009-0705-8_53)
---
### OSI
* Stands for **O**pen **S**ystems **I**nterconnect.
* A set of network protocols on 7 layers.
```
7. Application layer
6. Presentation layer
5. Session layer
4. Transport layer
3. Network layer
2. Data link layer
1. Physical layer
```
* Supported by CCITT - **C**omité **C**onsultatif **I**nternational **T**éléphonique et **T**élégraphique, an organization that sets international communications standards. , now known as ITU - **I**nternational **T**elecommunication **U**nion.
---
### Principal standards
* From the standards defined in this framework, the ones most used in Europe of 1990 were:
* X.25: Packet-switching protocol for WANs.
* X.29: Remote terminal access protocol.
* X.400: The universal protocol for e-mail. X.400 defines the envelope for e-mail messages so all messages conform to a standard format.
* X.500: An extension to X.400 that defines addressing formats so all e-mail systems can be linked together.
[Quoting weboedia for CCITT](https://www.webopedia.com/definitions/ccitt/)
---
### The RARE Association
* Stands for **R**éseaux **A**ssociés pour la **R**echerche **E**uropéenne.
* Formed in June 1986.
* It was a not-for-profit association of European NRENS - **N**ational **R**esearch and **E**ducation **N**etworks.
* First office was in the NIKHEF laboratory in Amsterdam.
* In October 1994 it became TERENA - **T**rans-**E**uropean **R**esearch and **E**ducation **N**etworking **A**ssociation .
* In October 2015, it again changed its name to GÉANT and at the same time acquired the shares of GEANT Limited (previously known as DANTE). [Recent lecture by GEANT CEO](https://indico.cern.ch/event/1083122/)
---
### What all this shows
* An intense effort to create European network standards.
* Strong influence by the PTTs - Post Telephone Telegraph.
* National and regional networks (mostly X.25-based) and influential research communities, like CERN, participated in this effort, e.g. ACONET for Austria, RedIRIS for Spain, ARIADNE for Greece, NORDUnet for the Scandinavian countries.
* Companies & communities had their own networks, e.g. EARN/BITNET, DECnet, ESNET, NSFNET, HEPnet.
* HEP in particular had the HTC - HEP Technical Committee.
* HTC-Mail was one of the Working Groups.
---

|  | |
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
**E**uropean **E**lectronic **M**essaging **A**ssociation - EEMA BRIEFING April 1993
---
### How did this resolve?
* The OSI transport protocol was not as efficient as TCP/IP.
* OSI would need many years to become mature.
* Performance and functionality requirements were pressing.
* One could say that the OSI ambition was relevant to today's anti-GAFAM (Google Apple Facebook Amazon Microsoft) efforts; even if the ambition were fulfilled, the GAFAM progress would not have slowed down, of course.
* The wind started to change in 1989. TCP/IP and Internet applications were _Open_ **AND** _existing_ **AND** _performant_ **AND** _easy to use_.
---
### The CERN Email gateway in 1989
---

---
### The CERN Email gateway in 1990
---

---
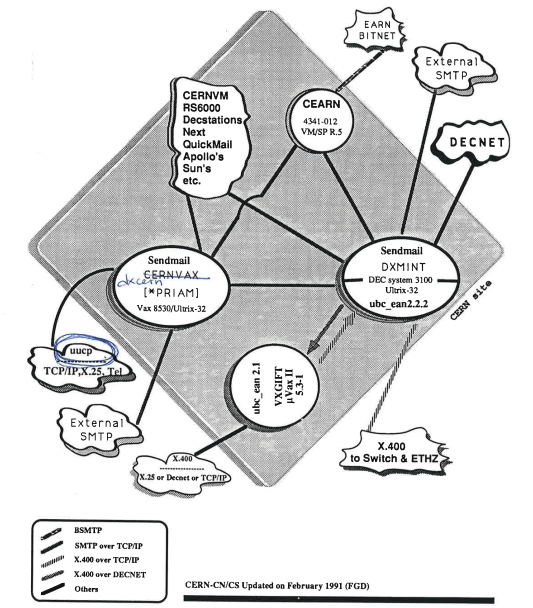
### The CERN Email gateway in 1991
---
---
### The CERN Email gateway in 1992
---

---
### How the addresses looked
**DECnet** _host::user_ - No hierarchy, at least in DECnet phase IV, host had to be unique.
**EARN/BITnet** _user@host_ (from within) _user@host.bitnet_
**X.400** _C=ch;ADMD=arcom;PRMD=cern;O=cern;OU=host;S=user;_
**UUCP** _user@host.uucp_ **OR** _host1!host2!...hostn!user_
**RFC822** (GEM - PEM) _name@domain - user@host.domain_
**PSI**mail - _PSI%DTEnumber::user **OR** PSI%host::user_
**GMAIL** - **G**eneral **M**ail _user@host.domain_ - A SLAC development, not used at CERN, for sending Email from VAX/VMS machines to BITNET or other networks. [See section 5 of this paper](https://cds.cern.ch/record/2804811/files/Names_related_to_computer_networks_at_cern_DIMOU_20jun1988.pdf).
**NB!** From JANET (the UK network) address was _user@ch.cern.host_
---
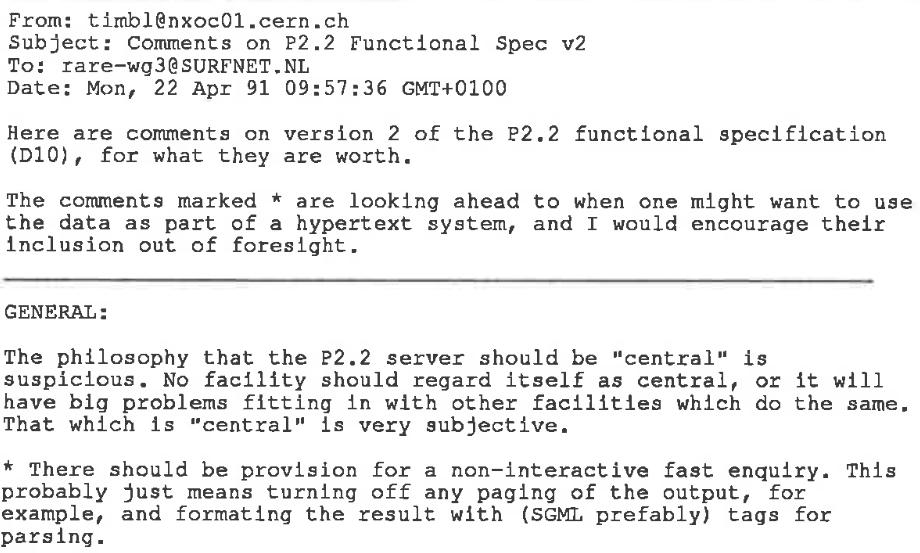
### Work with X.500 in the RARE Working Group WG3

See [full paper here](https://cds.cern.ch/record/2806388/files/)
---
### Attributes
A lot of work was devoted on
* _which_ attribute names to adopt.
* _which_ is the authority that gives values (at the time .gb vs .uk was still discussed)
* _how deep_ and _how flexible_ should the hierarchy of attributes be. Reason: They were used by X.400 Email, so there were matching requirements for the routing.
* Work done in the X.500 WG was very important for the definition of LDAP and X.509, used by today's certificates.
---
### Information Services work in the same WG
---
### The Web made that work much easier
* While Tim Berners-Lee was writing the Web code, this WG was making available catalogues of services.
* We were all discussing the contents and the conventions for these catalogues.
* There was a lot of maintenance in this work.
* It took a few years for the community to switch to the new mode of Information Services - alias The Web.
* Imagine the quality of life improvement, when publishing updates on paper became obsolete!
---
### Improvements - Utilities - Challenges
* All forwarding done by hand in a the DEC Ultrix DXMINT sendmail.cf file with regular expressions.
* When SMTP - **S**imple **M**ail **T**ransfer **P**rotocol and RFC822, i.e. username@domain were adopted, traffic increased and performance improved.
* Frédéric Hemmer wrote EMDIR - **E**lectronic **M**ail **DIR**ectory, which could be queried via Email.
* 1993 Summer Student George Melissargos wrote the _autorouter_ in C, a programme that turned the username@host.domain Email to [firstname.]surname@cern.ch.
---
### Communicating with the users
Mostly via the CNL - **C**omputer **N**ews**L**etter and the Userguides (on paper). Example:

---
### Challenges
* The team was always very small: Denise Heagerty handed over responsibility to Maria Dimou in 1988. Fellow Tor Bothner and a few collaborators were periodically joining.
* Bottlenecks = store & forward - were causing performance problems.
* Loops - the greatest and most frequent issue! Dietrich Wiegandt was The Email logs' Magus, he was reading core dumps like mystery novels.
* Incompatibility of network solutions and address syntax.
On the contrary **spam**, phishing and other security issues were not yet a concern.
The first large-scale commercial Email spam on the Internet appeared in 1994. (source: "Terena Celebrating 20 years" brochure)
---

---
### The Loop!
From newspaper THE INDEPENDENT Science column with title
"Short cut to chaos" and subtitle
"Darrel Ince writes on the chain reactions that are creating havoc in computer networks"
---
### Some pros of all this variety

Extract from Tim Berners-Lee’s talk at CERN Conference
“The role of Science in the Information Society” Dec. 2003
[Page 5 on my browser](https://cds.cern.ch/record/791186/files/p81.pdf)
---
### Science and Society - LBL Computing Newsletter December 1990

---
### Introducing Nathaniel Borenstein and MIME
In October 1990, Nathaniel presented "Why Do People Prefer FAX to Email?", to the IFIP WG 6.5 International Symposium on Message Handling Systems, Zurich, October 1990.
Maria presented [The Email Gateway Manager Reminiscent of Sisyphus](https://cds.cern.ch/record/211113/files/CM-P00065578.pdf)
Enjoy the history of **M**ultipurpose **I**nternet **M**ail **E**xtensions!
---