Opticsbuilder: build Synrad optics from sequence
===
[Opticsbuilder downloads](https://molflow.web.cern.ch/content/opticsbuilder-downloads)
# Adding elements
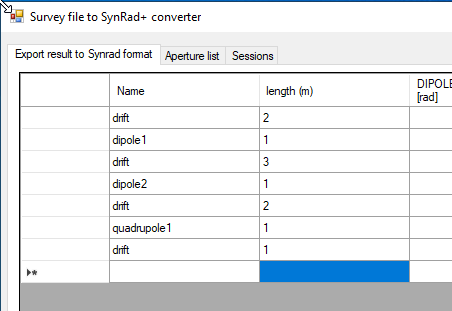
First fill names and lengths:
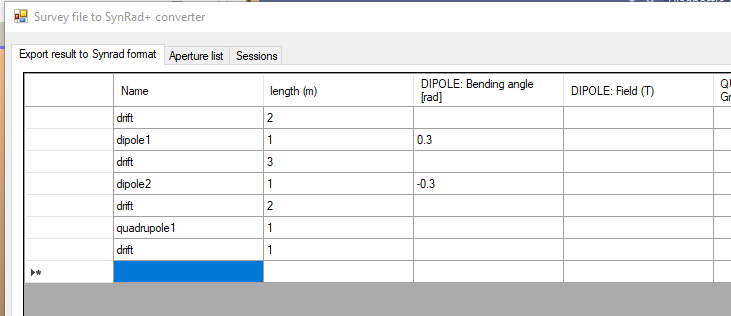
Add physical parameters:
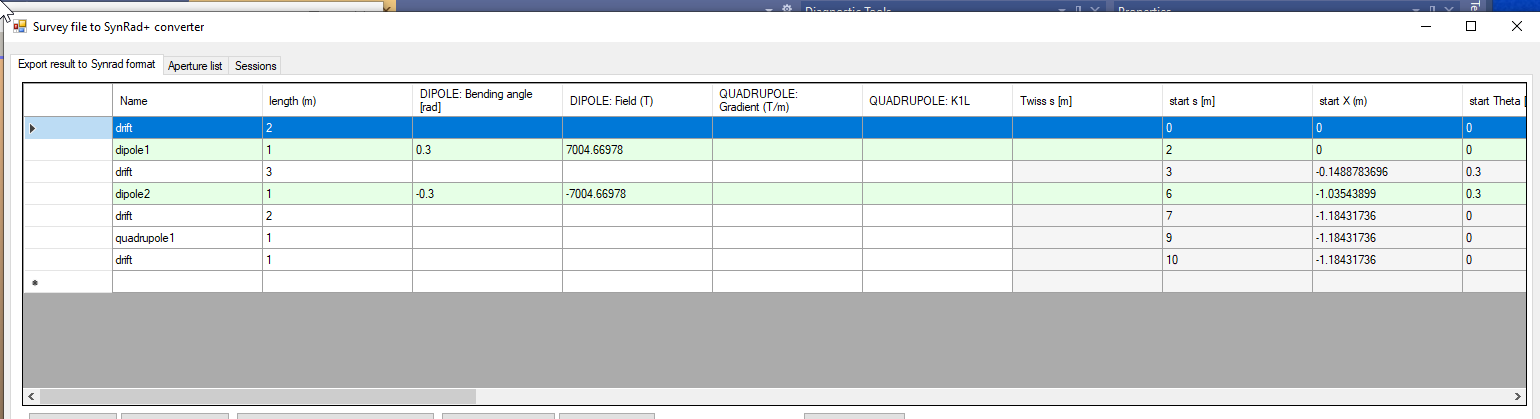
Set reference point by selecting a line (the first in this example), this is important as it will calculate element positions:


The grey fields show the calculated element positions:
# Adding lattice functions
They are required for a Synrad simulation (ideal beam not supported)
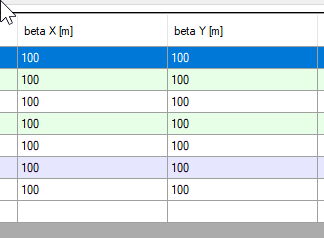
They are in meters, they must be positive.
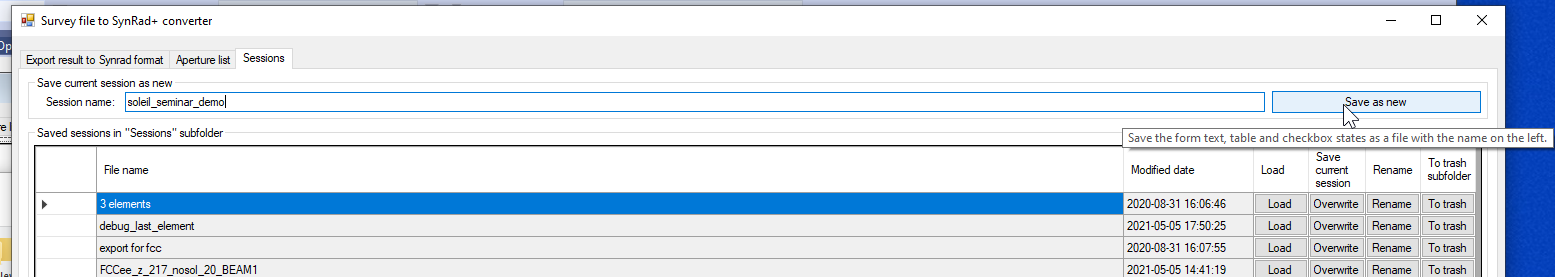
# Saving session
Opticsbuilder has a session manager, allowing you to save/load your work.
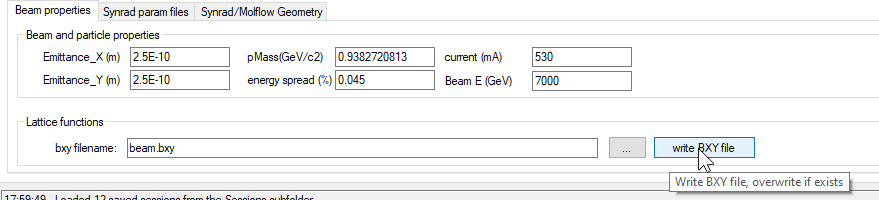
# Writing lattice functions file (.bxy)
First you have to write a BXY file, to be loaded by Synrad's `.param` files.
# Writing Synrad regions (.param and .mag)
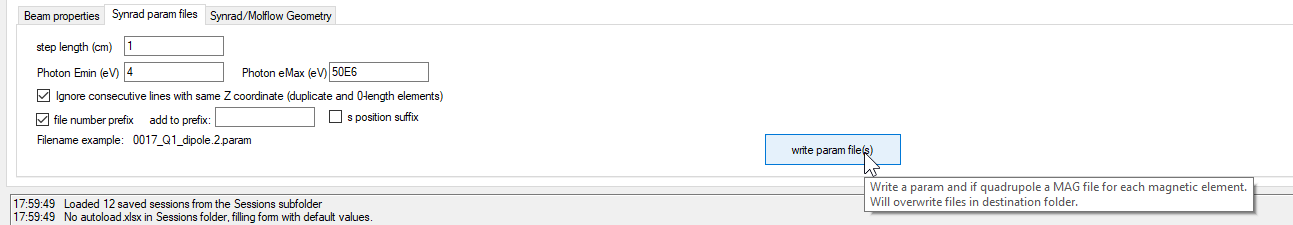
# Opening in Synrad
Use the Regions/Load command...
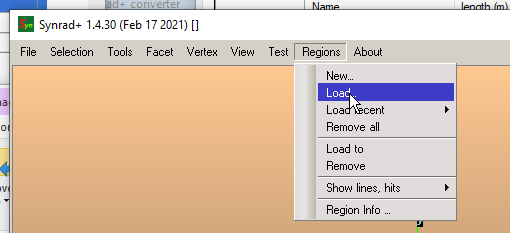
you can select all files at once:
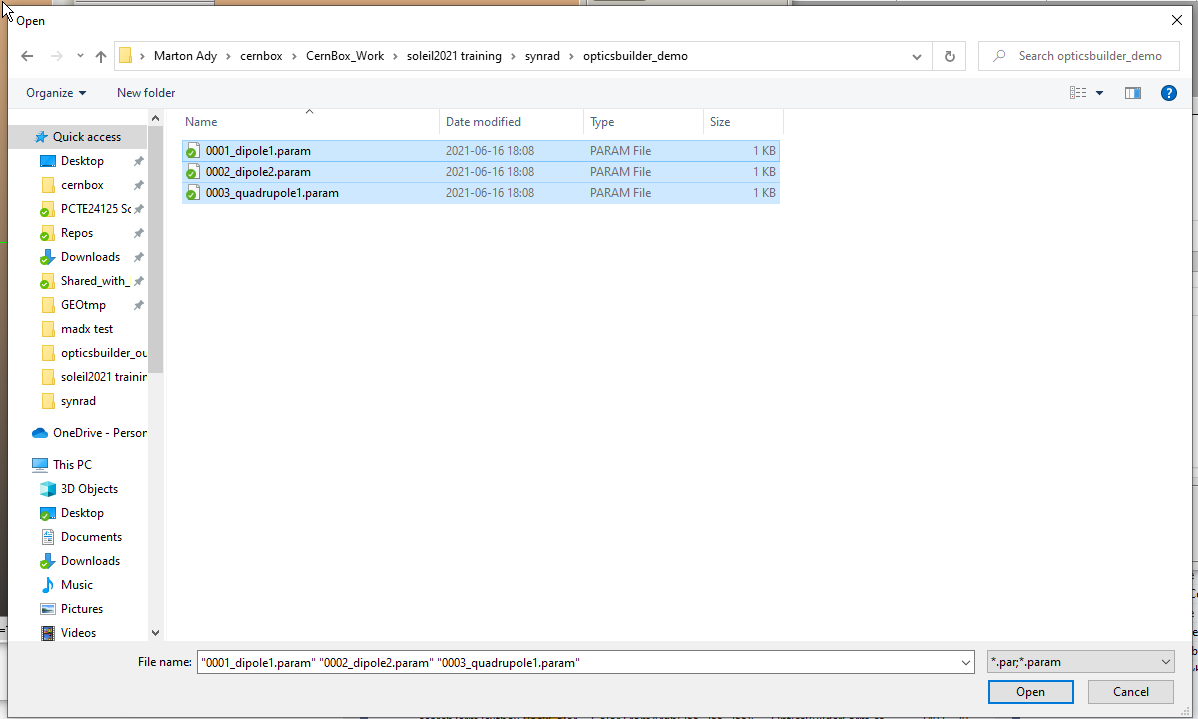
Synrad will load the magnetic regions.